The Humanitarian Crisis in Sudan: A Catastrophe Unfolding

The ongoing humanitarian crisis in Sudan has escalated into one of the most severe emergencies in recent history. The situation has deteriorated rapidly due to political instability, armed conflict, economic collapse, and natural disasters. Millions of people are facing acute food shortages, displacement, and a lack of essential services. The crisis has drawn the attention of the international community, yet efforts to mitigate the suffering remain insufficient. This article explores the roots of the crisis, its impact on the Sudanese population, and the urgent need for international intervention.
The Root Causes of the Crisis
Sudan has been plagued by political turmoil for decades. The country witnessed the ousting of long-time dictator Omar al-Bashir in 2019, followed by a fragile transitional government. However, tensions between the military and civilian leadership led to a military coup in October 2021, which derailed the democratic transition. The political instability has resulted in a power vacuum, allowing armed groups to exploit the situation, leading to violent clashes and widespread insecurity.
Furthermore, Sudan’s economy has been in freefall, with hyperinflation, food shortages, and a crumbling healthcare system. Sanctions, corruption, and mismanagement have exacerbated economic hardships, making it nearly impossible for ordinary Sudanese citizens to meet their basic needs. The situation has been worsened by climate change-induced droughts and floods, which have destroyed agricultural lands and disrupted food production.
Humanitarian Impact
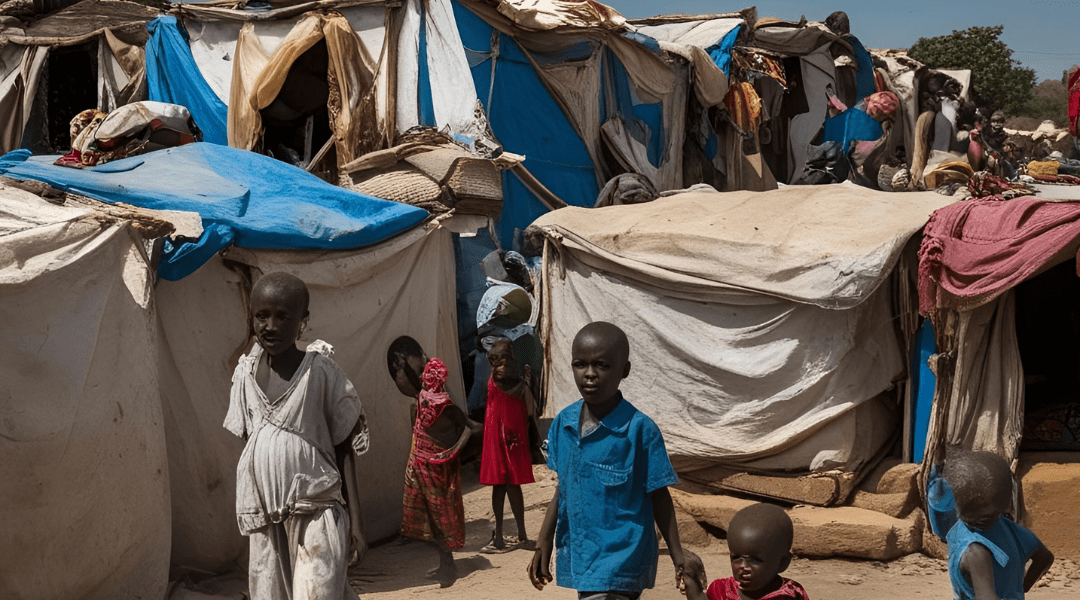
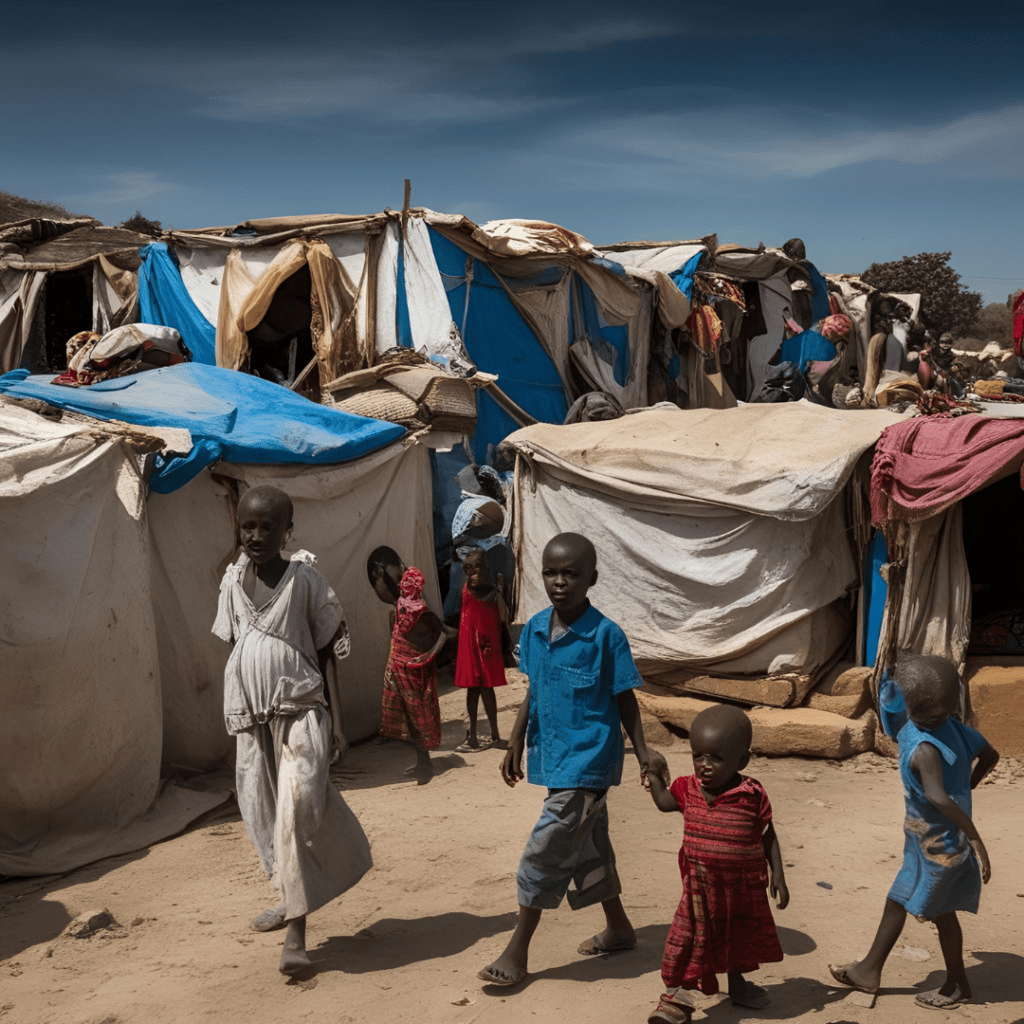
The impact of the crisis on Sudanese civilians has been devastating. According to humanitarian organizations, over 15 million people—nearly one-third of Sudan’s population—require urgent humanitarian assistance. The most vulnerable groups include children, women, and the elderly, who are suffering from malnutrition and a lack of medical care.
Food insecurity is a major concern, with the United Nations warning that millions are on the brink of famine. The collapse of supply chains and skyrocketing food prices have left families struggling to afford even a single meal per day. Malnutrition rates among children have surged, increasing the risk of preventable diseases and long-term developmental issues.
The conflict has also led to massive displacement. Over 4 million people have been forced to flee their homes, seeking refuge in makeshift camps or neighboring countries such as Chad, South Sudan, and Egypt. These refugees often lack access to clean water, sanitation, and adequate shelter, leaving them vulnerable to disease outbreaks.
Healthcare services in Sudan are on the verge of collapse. Many hospitals and clinics have been destroyed or shut down due to conflict and resource shortages. The limited medical facilities still operating face an acute shortage of medicines, medical personnel, and equipment. As a result, treatable illnesses and injuries are turning fatal.
International Response and Challenges
Despite the alarming humanitarian situation, the international response has been inadequate. Humanitarian aid has been hindered by logistical challenges, ongoing violence, and bureaucratic restrictions imposed by Sudanese authorities. Many aid organizations struggle to reach affected populations due to roadblocks, attacks on convoys, and limited funding.
The United Nations, along with various NGOs, has called for increased funding and support to address the crisis. However, donor fatigue and competing global crises, such as the war in Ukraine and the situation in Gaza, have diverted attention and resources away from Sudan. The African Union and regional organizations have attempted to mediate peace talks, but a lasting solution remains elusive.
The Need for Urgent Action
To prevent further suffering, immediate and coordinated international intervention is essential. The following measures should be prioritized:
- Increased Humanitarian Aid: The international community must ramp up funding for food assistance, medical aid, and shelter programs. More humanitarian corridors must be established to ensure aid reaches those in need.
- Diplomatic Pressure for Peace: Regional and global powers should intensify diplomatic efforts to broker a ceasefire and push for a return to democratic governance.
- Lifting of Aid Restrictions: The Sudanese government and armed groups must allow unhindered access to humanitarian organizations and ensure the safety of aid workers.
- Support for Refugees: Neighboring countries hosting Sudanese refugees should receive more financial and logistical support to manage the influx and provide adequate services.
- Long-Term Economic Support: International institutions should work on economic recovery programs that focus on rebuilding Sudan’s infrastructure, stabilizing its currency, and promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
Conclusion
The humanitarian crisis in Sudan is a catastrophe that demands immediate global attention. Without urgent action, millions will continue to suffer from hunger, displacement, and disease. The world cannot afford to ignore Sudan’s plight. It is imperative that governments, international organizations, and humanitarian agencies work together to provide relief and pave the way for a peaceful and stable future for Sudan.